On this page:
- Reducing your Drupal website’s carbon footprint
- Part 1 — Understanding the CO2 metric
- Part 2 — Drupal and the CO2 metric
- Part 3 — top 10 contributing factors to CO2 reduction
- Part 4 — the importance of reducing CO2 emissions
- Part 5 — Our contribution to reducing CO2 emissions
- Part 6 — How we can help you reduce your website's CO2 emissions
Reducing your Drupal website’s carbon footprint
Welcome to the sixth and final instalment of our comprehensive self-help guide series, focused on improving your Drupal website. In this 6-part series, we delve into six vital metrics for a successful Drupal website:
- Security
- Performance
- Accessibility
- Patches
- SEO
- Carbon emissions
In this guide we focus on carbon emissions. In recent years, there has been growing concern about the impact of websites on the environment. As the digital landscape continues to expand, so too does the carbon footprint of websites. Reducing CO2 emissions in web development is a critical aspect of minimising the environmental impact of digital activities and creating a more sustainable future for our planet.
In this insight, we explore the relationship between Drupal websites and carbon emissions. We discuss the importance of reducing CO2 emissions, the consequences of neglecting this metric, and the steps that can be taken to create a more eco-friendly website.
Go to our top 10 ways to reduce your Drupal website’s carbon footprint
Part 1 — Understanding the CO2 metric
What are website carbon emissions?
The CO2 metric refers to the measurement of carbon emissions produced by a during its operation. It includes the energy consumed by servers, data centres and end-user devices while browsing and interacting with the site. By measuring and reducing the CO2 emissions generated by a website, businesses can contribute to a more sustainable digital environment.
Why is the CO2 metric important?
Reducing CO2 emissions in web development is essential for several reasons:
Environmental impact: The internet consumes a significant amount of energy, resulting in increased greenhouse gas emissions. By optimising websites for reduced carbon emissions, businesses can help reduce the overall environmental impact of the digital world.
Corporate responsibility: With increasing awareness of climate change, many companies are prioritising sustainability and making efforts to reduce their carbon footprint. Focusing on the CO2 metric in web development can demonstrate a commitment to environmentally responsible practices.
User perception: A growing number of users are concerned about the environment and may be more inclined to engage with businesses that prioritise sustainability. A low-carbon website can help enhance a company's reputation and attract environmentally conscious customers.
Global authorities and guidelines
Various organisations provide guidelines and policies around sustainable web development, including:
- The Green Web : This organisation promotes sustainable web practices and provides a directory of green hosting providers to help businesses make eco-friendly choices.
- The Sustainable Web : The Sustainable Web Manifesto is a set of guiding principles that encourage businesses and developers to prioritise clean, efficient and sustainable web development practices.
Positive impact of CO2 reduction
Reducing the CO2 emissions of a website can lead to a variety of benefits, including:
Reduced energy consumption: Efficient websites consume less energy, resulting in decreased operating costs and a reduced environmental impact.
Improved user experience: Optimising a website for sustainability can also lead to performance improvements, resulting in faster load times and a better user experience.
Consequences of ignoring CO2 reduction
Neglecting the CO2 metric can result in:
Increased environmental impact: A website that fails to address its carbon footprint contributes to increased greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.
Negative brand perception: Ignoring sustainability concerns can lead to negative perceptions of a company's commitment to social responsibility, potentially harming its reputation and customer base.
Missed opportunities for optimisation: Websites that do not prioritise CO2 reduction may overlook potential improvements in performance, user experience, and other key metrics
Part 2 — Drupal and the CO2 metric
Drupal's capabilities and features for CO2 reduction
Drupal, as a leading open-source CMS, provides various capabilities, features and modules that can help address the CO2 metric:
Performance optimisation: Drupal's built-in performance optimisation features, such as caching and asset aggregation, can help reduce energy consumption by serving pages faster and more efficiently. View Drupal’s caching
Mobile-first approach: Drupal promotes a mobile-first approach in web development, allowing developers to create responsive designs that reduce energy consumption on mobile devices.
Eco-friendly modules: there are several Drupal modules dedicated to sustainability, including modules for image optimisation (such as image and responsive image ), lazy , and server resource .
Alignment with sustainable web guidelines
Drupal aligns with sustainable web development guidelines provided by organisations like the Green Web and the Sustainable Web . Its flexibility and customisation options allow developers to implement environmentally friendly practices in web development.
Well-known examples of successful CO2 reduction
One example of a Drupal website that’s reduced its CO2 emissions is:
Climate : This not-for-profit organisation focuses on climate action. The goal is net zero carbon emissions globally by 2050. View the Climate Group Drupal case
Poor examples of CO2 reduction
Some Drupal websites fail to prioritise sustainability and overlook the importance of CO2 reduction. Examples of practices that would lead to increased carbon emissions are:
Heavy, image-based websites: A Drupal website that relies heavily on high-resolution images without optimising them for the web may contribute to excessive energy consumption and slow page load times.
Inefficient coding practices: Poorly coded Drupal websites can result in slow performance and high energy usage due to inefficient server resource management and unoptimised assets.
Drupal version considerations
Different Drupal versions may have varying impacts on the CO2 metric:
Drupal 7: Drupal 7 provides basic performance optimisation features, but it may not be as efficient as later versions in terms of sustainability.
Drupal 8: Drupal 8 introduced significant improvements in performance and sustainability, including advanced caching mechanisms and mobile-first design approaches.
Drupal 9 and 10: Drupal 9 and 10 continue to build on the performance improvements of Drupal 8, offering even better optimisation features and support for eco-friendly modules to help reduce a website's CO2 emissions.
Part 3 — top 10 contributing factors to CO2 reduction
The top 10 ways to reduce the carbon footprint of your Drupal site are:
- Optimise images
- Enable caching
- Optimise CSS and JavaScript
- Implement server-level optimisation
- Choose green hosting
- Enable lazy loading
- Optimise database queries
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Monitor and optimise performance
- Choose energy-efficient themes and module
1. Optimise images
What it is: Images often account for a large portion of a website's energy consumption. Optimising them can help reduce the website's CO2 footprint.
Positive impact: Image optimisation improves website performance, resulting in lower energy consumption and faster page load times.
Steps to implement:
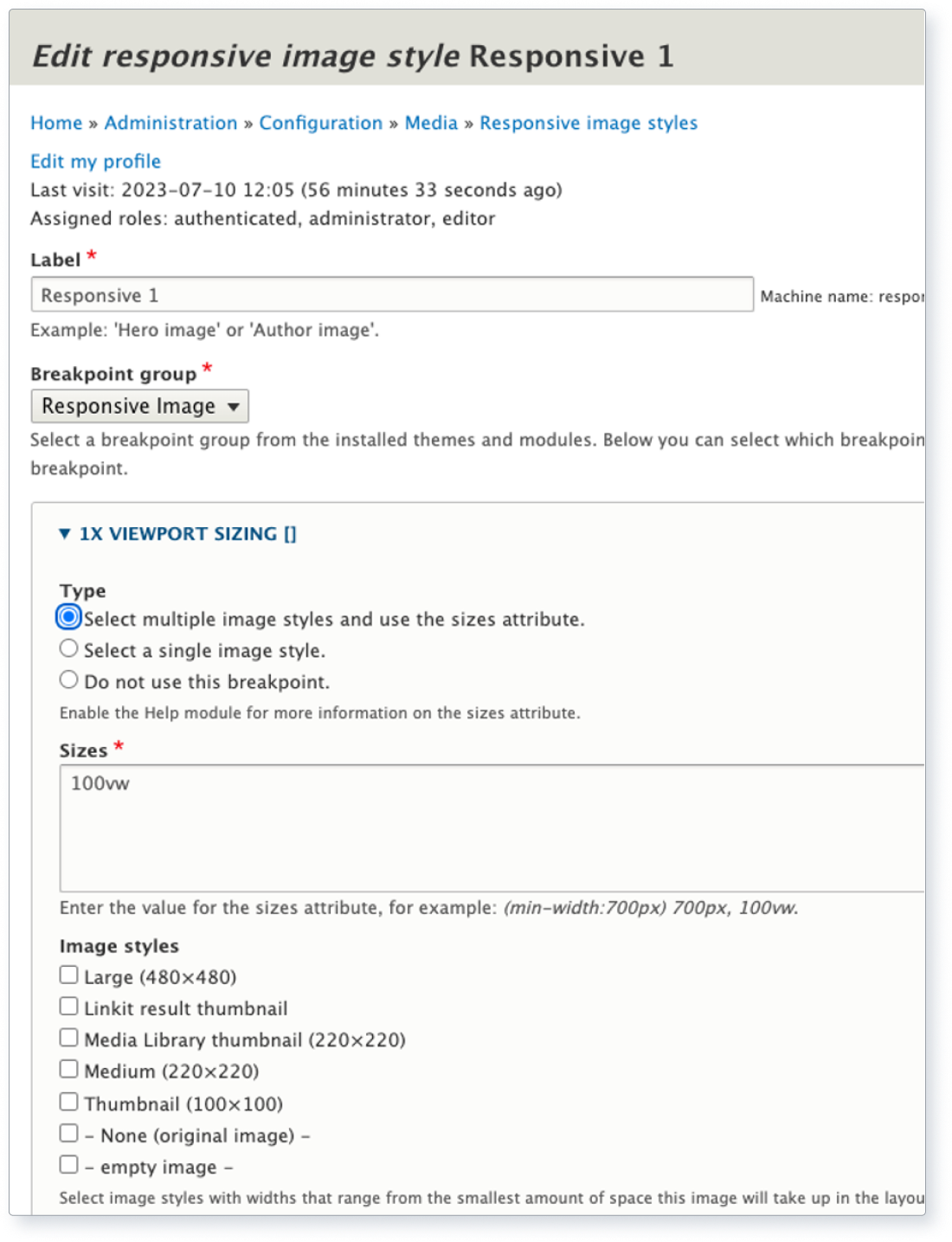
Implement responsive images using the 'srcset' attribute or Drupal's Core responsive image . With the responsive image module you can render images based on the screen size. For instance if someone is viewing your Drupal site on a mobile phone, it probably isn't necessary to show a full width hero image picture of 1920 x 1080 pixels. You can easily do with something smaller like 600 x 400 pixels. This cuts down the file size of the images your user has to download. Greener site, happy user and you’ll also get a thumbs up by Google when you check your Drupal site with PageSpeed .
Use appropriate image formats, such as WebP or AVIF, for better compression and performance.
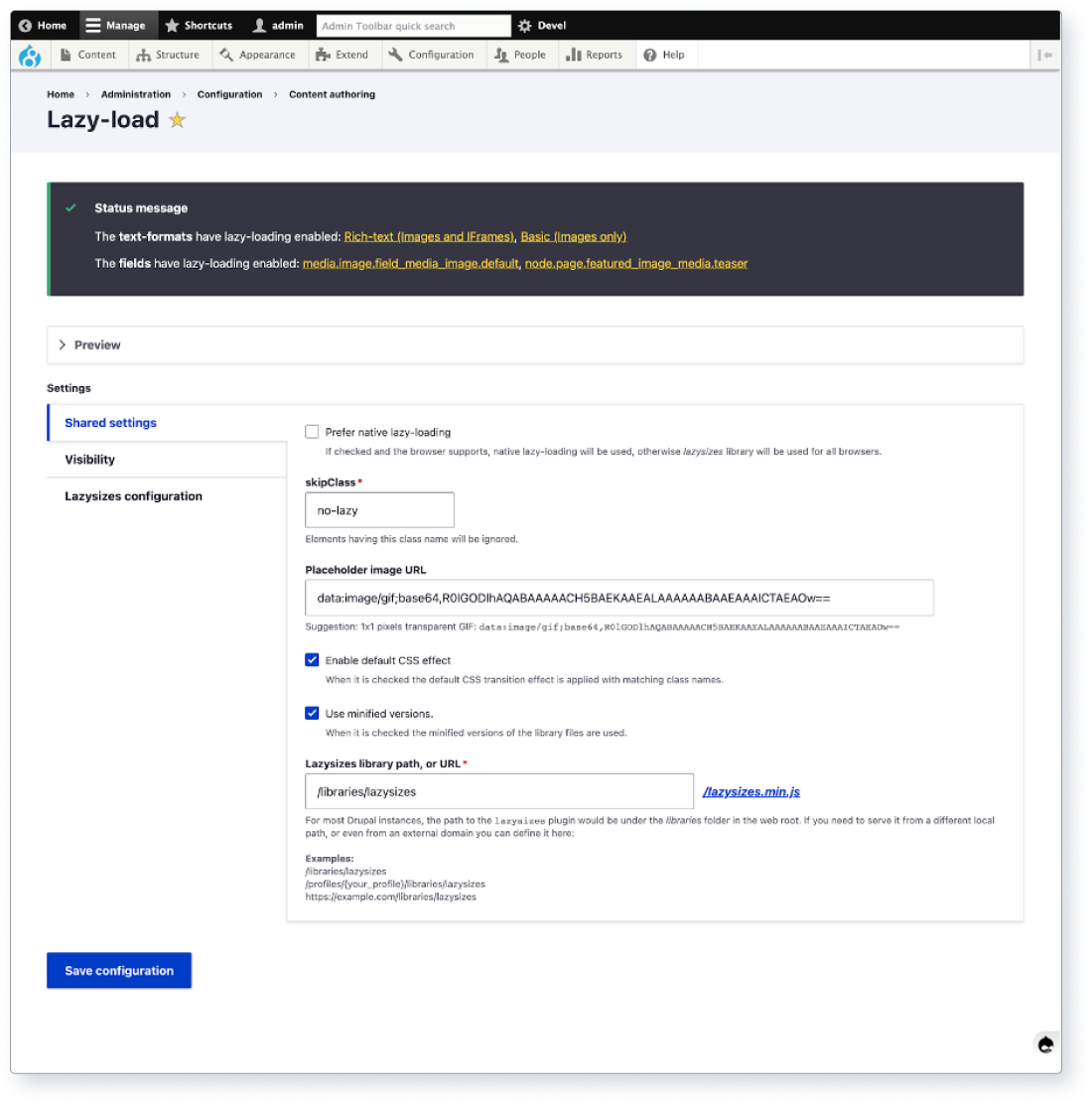
Use lazy to defer loading offscreen images until they’re needed.
Above: Screenshot of Drupal core’s responsive image module.
2. Enable caching
What it is: stores frequently used data to reduce server load and decrease page load times, which can help reduce a website's CO2 emissions.
Positive impact: Caching improves website performance and reduces energy consumption by serving previously-rendered content without the need to regenerate it.
Steps to implement:
- Enable Drupal's built-in caching in the configuration settings.
- Implement a reverse proxy cache to further improve caching efficiency.
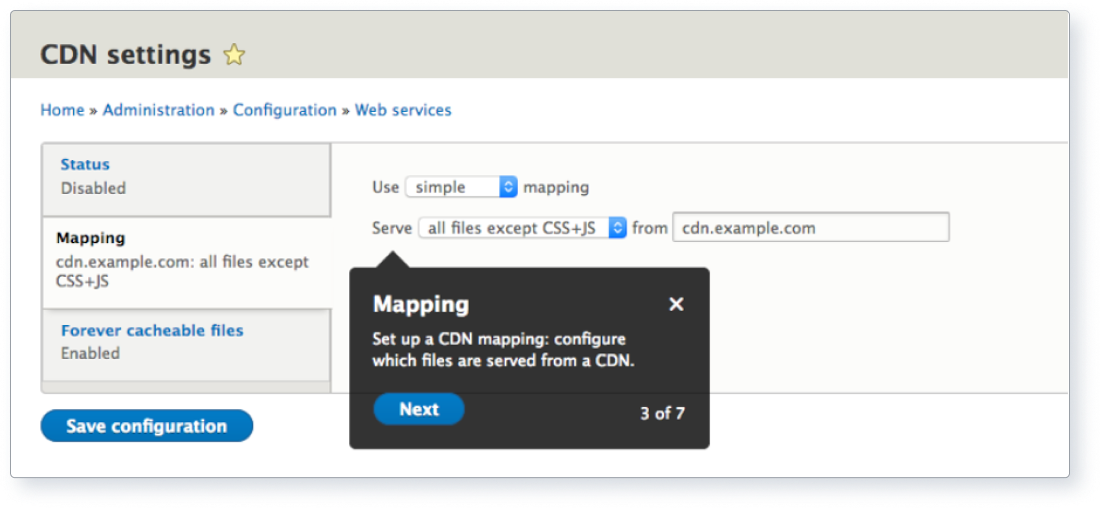
- Use Content Delivery (CDNs) to cache and deliver static assets, reducing latency and energy consumption.
Above: Screenshot of CDN settings that enable caching.
3. Optimise CSS and JavaScript
What it is: Optimising and files can help reduce a website's energy consumption.
Positive impact: Minifying and aggregating CSS and JavaScript files can lead to faster page load times and lower energy consumption.
Steps to implement:
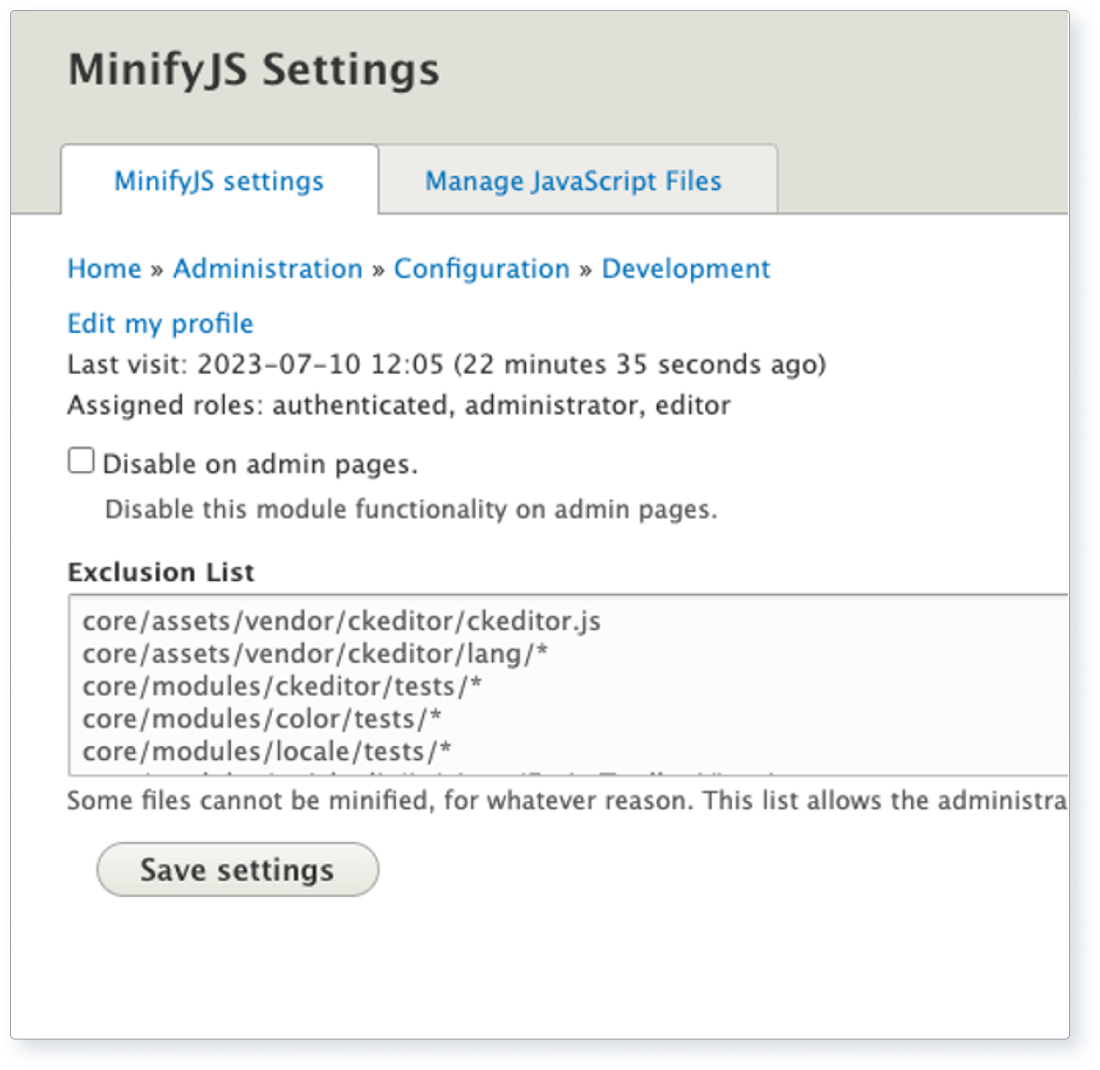
- Enable Drupal's built-in aggregation settings for CSS and JavaScript files.
- Use tools like or to minify files further.
- Eliminate unused CSS and JavaScript code using tools like or .
Above: Screenshot showing the configuration for minifying JS using the contributed module Minify JS.
4. Implement server-level optimisation
What it is: Optimising server configurations can help reduce a website's CO2 emissions.
Positive impact: A properly configured server improves website performance and reduces energy consumption by using resources more efficiently.
Steps to implement:
- Use PHP 8 or later for better performance and energy efficiency.
- Enable HTTP/2 for faster and more efficient resource delivery.
- Implement server-level caching solutions, such as or .
5. Choose green hosting
What it is: Selecting a green hosting provider can help reduce a website's CO2 footprint.
Positive impact: Green hosting providers use energy-efficient infrastructure and often offset their energy consumption with renewable energy credits.
Steps to implement:
- Research hosting providers that prioritise sustainability and use green technologies.
- Review their energy efficiency practices and renewable energy credits.
- Migrate your website to the selected green hosting provider.
Above: Screenshot showing details of how Salsa Hosting improves a website’s carbon footprint.
6. Enable lazy loading
What it is: Lazy loading defers the loading of non-critical assets until they’re needed, which can help reduce a website's CO2 emissions.
Positive impact: Lazy loading reduces energy consumption by only loading content when it’s actually required, resulting in faster page load times and improved user experience.
Steps to implement:
- Identify non-critical assets, such as images or videos, that can be lazy-loaded.
- Implement a lazy loading solution, like the Drupal Lazy Load or using JavaScript libraries like Intersection Observer or Lozad.js.
- Test your website to ensure lazy loading is working as expected and improving performance.
Above: Screenshot of Drupal Lazy Load module.
7. Optimise database queries
What it is: Efficient database queries can help reduce a website's CO2 emissions by minimising the amount of processing power required.
Positive impact: Optimising database queries reduces server load and energy consumption, improving website performance and sustainability.
Steps to implement:
- Review database queries for inefficiencies and bottlenecks using tools like the Drupal Devel or MySQL's EXPLAIN .
- Optimise queries by using indexes, limiting result sets and avoiding nested loops or unnecessary joins.
- Monitor database performance to ensure optimisations are effective and maintainable.
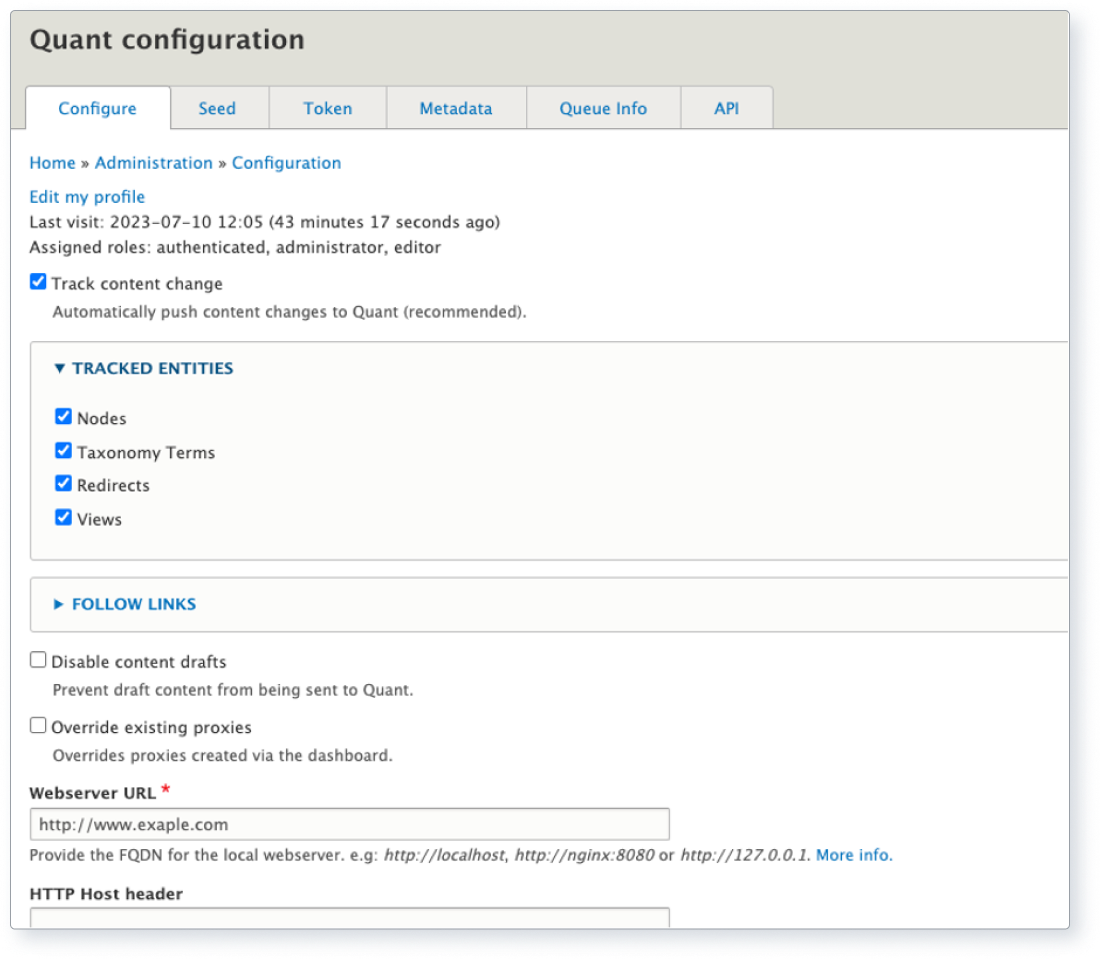
8. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
What it is: Using a CDN can help reduce a website's CO2 emissions by serving content from geographically distributed data centres.
Positive impact: CDNs reduce energy consumption by delivering content from a location closer to the user, resulting in faster page load times and improved user experience.
Steps to implement:
- Choose a reputable CDN provider, such as , or Amazon .
- Configure your CDN to serve your website's static assets, such as images, stylesheets and JavaScript files.
- Test your website to ensure the CDN is working correctly and improving performance.
Above: Screenshot of QuantCDN’s configuration settings.
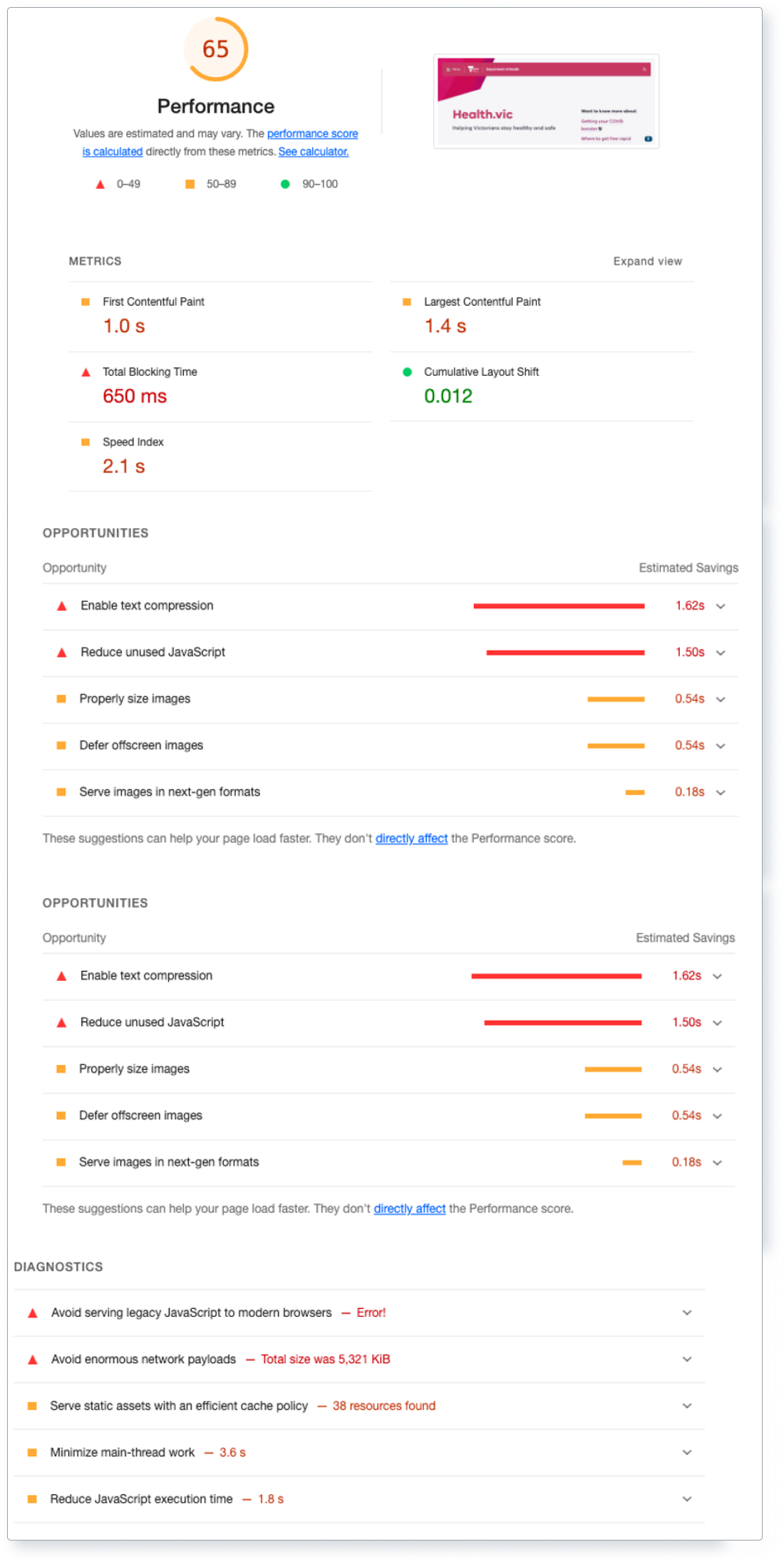
9. Monitor and optimise performance
What it is: Regularly monitoring and optimising website performance can help reduce a website's CO2 emissions.
Positive impact: Continuous performance optimisation ensures a website remains energy efficient and delivers a better user experience.
Steps to implement:
- Use performance monitoring tools like Google , or to analyse your website's performance.
- Identify areas for improvement and implement optimisations, such as image optimisation, caching or minification.
- Re-test and monitor website performance regularly to maintain energy efficiency.
Above: Screenshots of sample Lighthouse report.
10. Choose energy-efficient themes and modules
What it is: Selecting energy-efficient themes and modules can help reduce a website's CO2 emissions.
Positive impact: Energy-efficient themes and modules improve website performance and reduce energy consumption, contributing to a more sustainable website.
Steps to implement:
Research Drupal themes and modules that prioritise performance and energy efficiency.
Test themes and modules for performance impact and compatibility with your website.
Implement energy-efficient themes and modules on your website, replacing less efficient alternatives.
Use dark colours: With OLED screens becoming more popular, using darker colours can help save energy. This is because when an OLED screen shows a black pixel it's turned off. Try to go with dark background colours and use a brighter colour for your text. Seeing the implementation of dark mode in browsers and mobile phones this might be an indication that users prefer darker colours.
Use modern CSS techniques: Using techniques such as and can cut down the number of lines of code you need to create your Drupal theme. These new techniques are more efficient and pretty well supported by most major browsers.
Avoid unnecessary JavaScript: Cramming in different snippets of JavaScript can easily add to your page weight. Do you still have jQuery Carousel showing important content on your homepage? Dump it. Usability experts say it doesn't work. Or maybe you forgot about that tracking script of a service you don't use anymore. Time to review all the scripts you've added to your Drupal website along the way.
Part 4 — the importance of reducing CO2 emissions
Reducing a website's CO2 emissions is crucial for improving its environmental impact and sustainability. By implementing the strategies mentioned above, website owners can optimise performance, decrease energy consumption and contribute to a greener internet.
You’ll reduce your website's carbon footprint and also enhance its performance and user experience, ultimately benefiting both your business and your customers.
Follow the 10 steps in this self-help guide and you’ll be well on your way to a greener, more efficient and more successful Drupal website.
Part 5 — Our contribution to reducing CO2 emissions
As a Drupal development agency, we’re committed to helping our customers and the wider Drupal community create sustainable websites. We proudly showcase our contributions to this metric, providing specific examples of our work and case studies that demonstrate our commitment to reducing CO2 emissions.
Our three main areas of contribution are:
1. Drupal360.io: a comprehensive audit tool
Our audit tool, Drupal360.io, has been designed to help you assess your site's performance across all six critical metrics, including CO2 emissions. By using Drupal360.io, you can gain valuable insights into the areas where your website needs improvement and receive actionable recommendations to enhance its overall sustainability. Drupal360 is currently in the final stages of development and an alpha version will be released within the next month.
We take pride in being active contributors to the Drupal community, sharing our expertise and knowledge. One example of this is our blog:
The social impact of open source
Above: Screenshot from a Salsa blog on the social impact of open source.
Part 6 — How we can help you reduce your website's CO2 emissions
Our team of experts is here to help you reduce the carbon footprint of your website.
Our Drupal CO2 services include:
1. Salsa Support
Salsa Enterprise Drupal Support can be used to draft a CO2 fixes and improvements plan that includes regular audits and best practices.
2. CO2 emission audit
Our team of experts will perform a comprehensive audit of your Drupal website, analysing its CO2 emissions and identifying the key contributing factors. We'll provide a detailed report on our findings and suggest tailored, actionable recommendations to help you reduce your website's carbon footprint.
3. Green hosting solutions
Salsa's Drupal enterprise hosting platform implements several unique features that significantly reduce a website's carbon footprint.
More about Salsa Hosting
More information on Salsa’s services to reduce your carbon footprint
By using our Drupal360.io audit tool and following the guidelines provided in this self-help series, you can join us in the fight against climate change. Together, we can create a greener, more sustainable internet that benefits both the environment and the millions of users who rely on it every day.